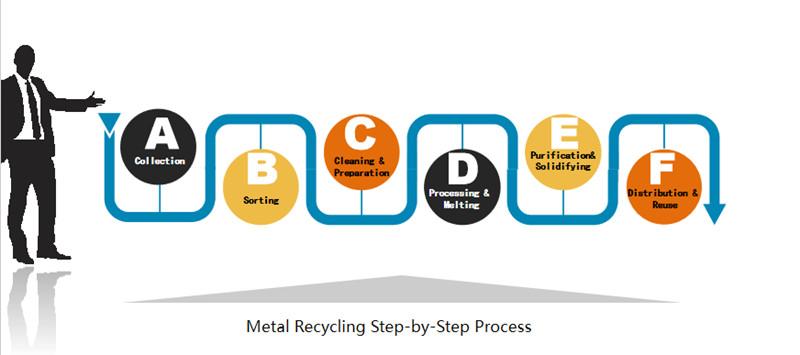
How Metal Recycling Affects the Environment and Our Lives

1. Which metals can be recycled?
Most metals around us can be recycled. The most common ones are aluminum, steel, copper, stainless steel, and titanium. Recycling these metals helps protect the environment. It also saves a lot of energy.
Aluminum is one of the easiest metals to recycle. Cans, foil, and car parts can all go back into the system. Recycled aluminum can be used again and again without losing quality.
Steel and stainless steel are used in buildings, cars, and appliances. Recycled steel can be made into new beams, machines, and tools.
Copper is found in wires, pipes, and electronics. Recycling copper helps reduce mining and cuts down on cost.
Even titanium, which is used in high-end industries, is becoming easier to recycle thanks to new technologies.

2. Which metals cannot be recycled?
Some metals are hard to recycle. This is usually because they contain special additives or have been contaminated.
Certain aerospace or military alloys are too complex to break down. Magnesium and some aluminum alloys can produce harmful byproducts when recycled.
If metals are mixed with oil, paint, or coatings, they can’t go straight into the recycling process. They need special treatment first. That makes recycling more expensive and less efficient.
3. Is recycling metal a good thing?
Yes—recycling metal is one of the most effective ways to conserve resources and reduce environmental impact. It helps save raw materials, cuts energy use, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
For example, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from bauxite. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA, 2021), recycling 1 ton of aluminum can save around 14,000 kWh of electricity. That’s enough to power a home for nearly a year. It also prevents up to 10 tons of CO₂ emissions, significantly reducing our carbon footprint 11.
Aluminum is especially efficient because it can be recycled infinitely without losing strength, corrosion resistance, or quality. This makes it a perfect example of circular economy in action.
Steel is another highly recycled material. The Steel Recycling Institute (2023) reports that recycling 1 ton of steel saves about 1,100 kWh of energy and reduces 0.5 tons of CO₂ emissions 22. In the United States, more than 70% of steel is made from recycled scrap, largely thanks to energy-efficient electric arc furnace (EAF) technology 33.
Recycled copper is also widely used in wires, electronics, and plumbing systems. It’s much cheaper than mining new copper and helps reduce the environmental impact of large-scale mining. As copper prices continue to fluctuate, recycled copper provides a more stable and eco-friendly alternative.
Besides saving energy, recycling metal also helps reduce landfill waste. According to The World Bank (2018), metal waste accounts for about 10% of global solid waste by volume, especially in cities where construction and electronic waste are rising rapidly 44. Instead of taking up space and risking pollution, these metals can be reused in manufacturing, helping achieve zero-waste and green economy goals.
4. What can recycled metals be used for?
Recycled metals are everywhere. You probably use them every day without knowing.
Aluminum cans are one of the most common recycled products. Most drink cans you use today come from recycled metal.
Cookware like pots, pans, baking sheets, and foil can be made from recycled aluminum too.
Home appliances—such as fridges, washing machines, and microwaves—use lots of recycled steel and aluminum in their frames and parts.
Electronics also contain recycled metals. Phones, TVs, and laptops have copper and aluminum parts made from recycled sources.
Cars are another big user. Many car bodies and engines are made from recycled steel and aluminum. Brands like BMW and Toyota use a lot of recycled materials to save costs and reduce emissions.
These examples show how recycling gives metal a new life—and helps us build a greener, more sustainable world.
5. What are the disadvantages of recycling metal?
Recycling metal is great—but not perfect. There are some downsides too.
One issue is quality. Recycled metals might have small amounts of unwanted materials. That can affect the strength or purity of the final product.
Some metals are also hard or expensive to recycle. Rare metals or complex alloys need special equipment. That adds to the cost.
Also, while recycling saves energy overall, some parts of the process—like melting—can still create pollution. If not managed well, this can harm the environment.
So while metal recycling is a smart and green choice, it still needs proper technology and management to avoid new problems.
6. What You Can Do: Everyday Metal Recycling Tips
Recycling metal at home is easier than you might think. Many everyday items—like soda cans, food tins, old phone chargers, broken scissors, or even worn-out kitchen tools—contain metal that can be recycled. Instead of throwing them in the trash, collect them in a box or bag and drop them off at your local recycling center or scrap collection point.
A few simple habits can make a big difference. Rinse out cans before recycling to remove food or drink residue. Separate metal items from plastic or paper packaging so the recycling process is more efficient. If you have larger items like appliances or electronics, check if your city offers special e-waste collection days, or bring them to a certified e-waste recycling facility.
These small actions might seem minor, but when done by millions of people, they have a real impact. Recycling metal not only saves natural resources and energy—it helps reduce pollution and supports a cleaner, more sustainable future. Every can, cable, or toaster you recycle counts.
At Shenzhen Chinalco Metal, we don't trade in scrap metal. Instead, we focus on supplying high-quality aluminum and titanium products for demanding applications in aerospace, defense, and precision manufacturing. Our materials are made from virgin metals to ensure performance, consistency, and traceability. If you're looking for premium-grade aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, or custom machining services, feel free to contact us—we're here to help
1,U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Aluminum Recycling Facts. Retrieved from www.epa.gov, 2021.
, Steel Recycling Institute. Benefits of Steel Recycling. www.recycle-steel.org, 2023.
, American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI). Steel Industry Data 2023.
, The World Bank. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. 2018.