What is TA5 titanium and it's difference with TC4?

A Comprehensive Overview of TA5 Titanium Alloy
TA5 titanium alloy, also known as Ti-5Al, is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and weldable α-type titanium alloy. It is widely used in aerospace, shipbuilding, and chemical equipment industries due to its excellent mechanical properties, good formability, and superior resistance to corrosion. In this article, we will explore the key features, properties, and applications of TA5 titanium alloy.
1. Chemical Composition of TA5 Titanium Alloy
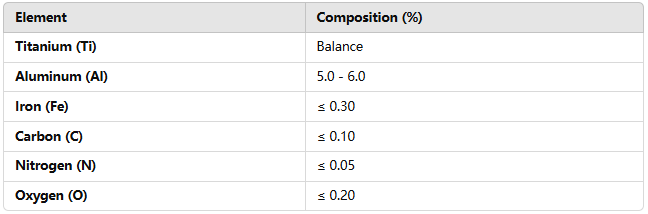
TA5 titanium alloy is primarily composed of titanium (Ti) and aluminum (Al), with small amounts of other elements, such as iron (Fe), oxygen (O), carbon (C), and nitrogen (N). These elements contribute to the alloy's high strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent processing properties.
2. Mechanical Properties
TA5 titanium alloy is renowned for its high strength and excellent toughness. Its tensile strength typically ranges between 685 MPa and 800 MPa, while its yield strength is between 585 MPa and 650 MPa. The alloy also demonstrates good ductility, with an elongation of 15% or higher, and a reduction of area greater than 40%, making it resistant to fracture under stress.
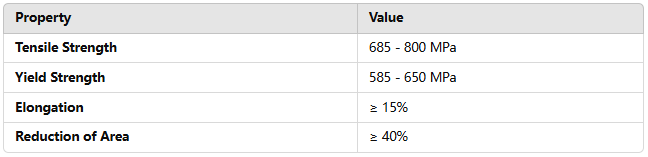
3. Physical Properties
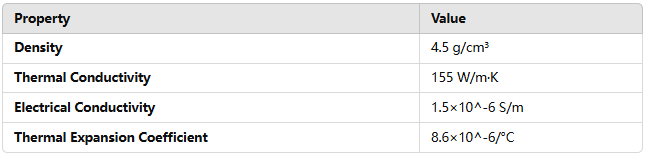
TA5 titanium alloy offers excellent physical properties, including a relatively low density of 4.5 g/cm³, making it both lightweight and strong. Its thermal conductivity is approximately 155 W/m·K, and its electrical conductivity is about 1.5×10^-6 S/m, typical for titanium alloys. Additionally, the coefficient of thermal expansion is low, at about 8.6×10^-6/°C, which helps maintain stability under temperature variations.
4. Corrosion Resistance
One of the key advantages of TA5 titanium alloy is its excellent corrosion resistance. The alloy has high resistance to a range of corrosive environments, including oxidation, nitric acid, chloride solutions, and other aggressive chemical media. This makes TA5 an ideal material for applications in harsh environments, such as in marine, chemical, and aerospace industries.
5. Heat Treatment and Processing
TA5 titanium alloy can be heat-treated to improve its mechanical properties. Common heat treatment processes include solution treatment and aging treatment, which enhance the alloy's strength and hardness. These heat treatments enable TA5 to perform well under demanding conditions while maintaining a high level of toughness and fatigue resistance.
The alloy is also easy to process and can be formed through various manufacturing techniques such as forging, stretching, and rolling. This makes TA5 a versatile material for producing components of various shapes and sizes.
6. Weldability
TA5 titanium alloy is known for its good weldability. It can be welded using a variety of techniques, including argon arc welding, electron beam welding, and laser welding. This makes TA5 highly versatile for joining parts in critical applications where the strength and integrity of the weld are essential.
7. Applications of TA5 Titanium Alloy
TA5 titanium alloy is primarily used in industries where high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good weldability are required. Its wide range of applications includes:
Aerospace Industry: Engine components, airframes, and other structural elements in aircraft and spacecraft.
Shipbuilding: Parts exposed to harsh marine environments, where resistance to corrosion is crucial.
Chemical Equipment: Tanks, piping, and reactors that need to withstand aggressive chemical environments.
Key Differences Between TA5 Titanium and TC4:
Mechanical Strength: TA5 has higher tensile and yield strength than TC4, making it more suitable for high-stress applications.
Density: TA5 is slightly denser than TC4, though the difference is marginal.
Corrosion Resistance: TA5 has superior corrosion resistance compared to TC4, making it more suitable for highly corrosive environments like marine and chemical industries.