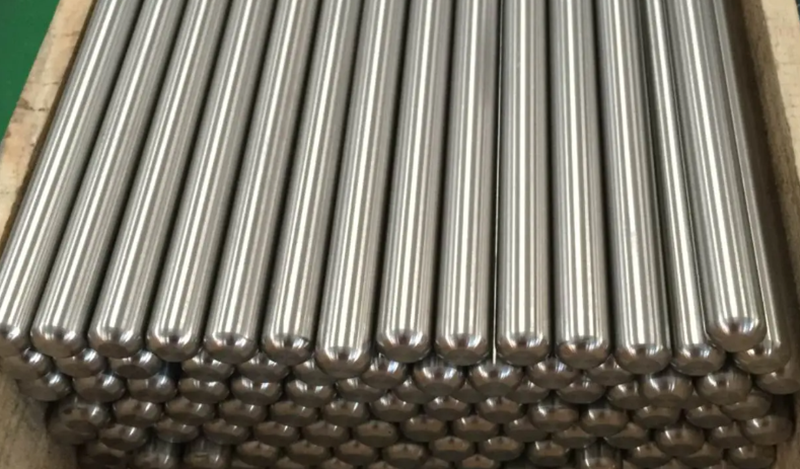
What is TC4 Titanium Alloy?

TC4 titanium alloy, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is a widely used α-β titanium alloy that consists of two phases: the α phase (alpha) and the β phase (beta). This alloy contains approximately 6% aluminum (Al), which stabilizes the α phase, and 4% vanadium (V), which stabilizes the β phase. TC4 is renowned for its excellent combination of mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and good weldability, making it ideal for applications in demanding industries like aerospace and aviation.
Key Properties of TC4 Titanium Alloy
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: TC4 titanium alloy exhibits outstanding strength and relatively low density, which makes it ideal for aerospace applications where weight is a critical factor.
Good Corrosion Resistance: The alloy has excellent resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments, making it suitable for use in marine, chemical, and aerospace applications.
Good Machinability: TC4 has good plasticity, which allows it to be easily processed through various manufacturing methods, such as forging, welding, and machining.
Temperature Resistance: TC4 titanium alloy can withstand temperatures of up to 400°C for extended periods, which makes it particularly useful in high-temperature environments like turbine engines and compressor blades.
Weldability and Superplasticity: It exhibits excellent weldability and superplasticity, allowing for various processing techniques including forging, extrusion, and wire drawing.
Typical Applications of TC4 Titanium Alloy
Due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, TC4 alloy is widely used in the aerospace and aviation industries. Common applications include:
Engine Components: Such as fan and compressor disks and blades.
Structural Parts: Including beams, joints, and frames in aircraft structures.
Pressure Vessel Components: Due to its excellent combination of strength and light weight.
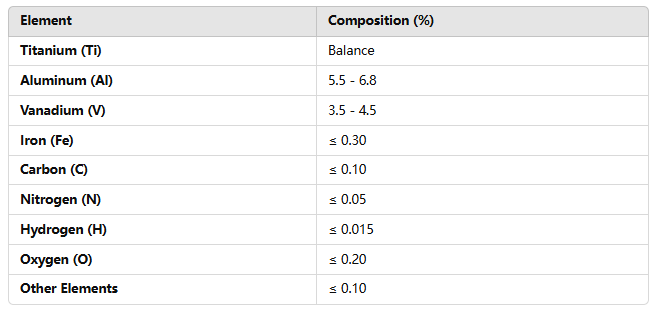
Chemical Composition of TC4 Titanium Alloy
The chemical composition of TC4 titanium alloy is designed to optimize its strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. The alloy mainly contains aluminum (Al) and vanadium (V), with trace elements to enhance specific properties.
Phase Transformation and Microstructure
TC4 titanium alloy exhibits a dual-phase microstructure, consisting of α (alpha) and β (beta) phases. The alloy undergoes a phase transformation from α + β → β during heat treatment, where the material is heated to high temperatures, causing the α phase to dissolve into the β phase. This transformation enhances the alloy's strength and toughness, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
α Phase (Alpha): The alpha phase is stable at lower temperatures and provides high strength and good ductility.
β Phase (Beta): The beta phase is stabilized by elements such as vanadium and offers higher strength at elevated temperatures.
The alloy can be processed to achieve a fine balance between strength, toughness, and ductility by controlling the ratio of α and β phases. In the annealed or solution-treated state, TC4 alloy shows good formability and is suitable for pressure processing methods such as forging, rolling, and extrusion.
Conclusion
TC4 titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) is one of the most widely used titanium alloys due to its excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and ability to perform in high-temperature environments. Its outstanding strength-to-weight ratio and good machinability make it ideal for aerospace applications, such as engine parts, structural components, and other high-performance uses. The precise chemical composition and phase transformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy are key factors in its exceptional performance in these demanding environments.
