What is the difference between aluminum fabrication and machining?

The Difference Between Aluminum Fabrication and Aluminum Machining
When working with aluminum, it’s essential to understand the distinction between fabrication and machining, as these processes serve different purposes and involve unique techniques. Both play crucial roles in creating aluminum components, but their approaches, scopes, and outcomes differ significantly.
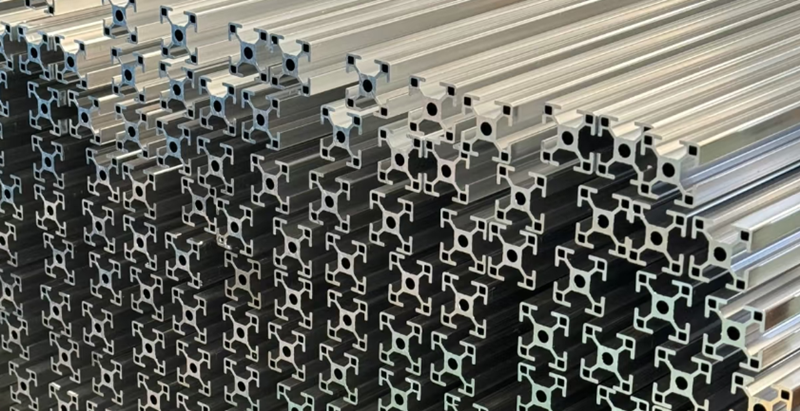

1. Aluminum Fabrication
Fabrication refers to the comprehensive process of transforming raw aluminum materials into finished products. It encompasses a wide array of manufacturing steps and techniques, often combining multiple processes to achieve the desired structure or functionality.
Key Characteristics of Aluminum Fabrication:
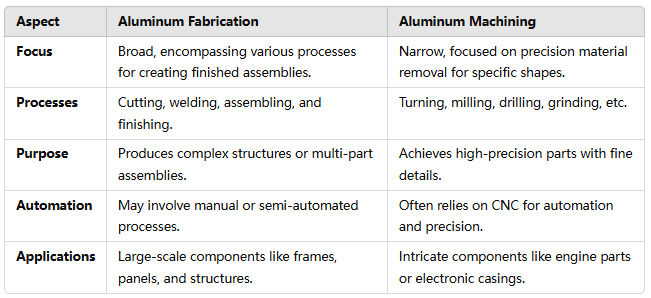
Scope of Work: Fabrication is a holistic process that includes designing, cutting, shaping, assembling, and finishing. It often integrates techniques such as welding, bending, extrusion, and surface treatments.
Purpose: The goal is to create an entire component or system. Aluminum fabrication is commonly used in industries such as construction, aerospace, and automotive, where large or complex assemblies are required.
Processes Involved:
Cutting: Using laser cutters, saws, or water jets to achieve precise dimensions.
Welding and Joining: Connecting parts using techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, ensuring strong and clean seams.
Assembly: Combining various pre-fabricated parts to create the final product.
Flexibility: Aluminum fabrication often involves customization for projects where the design and structure must meet specific functional requirements.
Applications of Aluminum Fabrication:
Fabrication is ideal for creating large-scale components such as aluminum frameworks, aircraft fuselages, and structural supports. It allows for integrating multiple processes to meet varied design specifications.
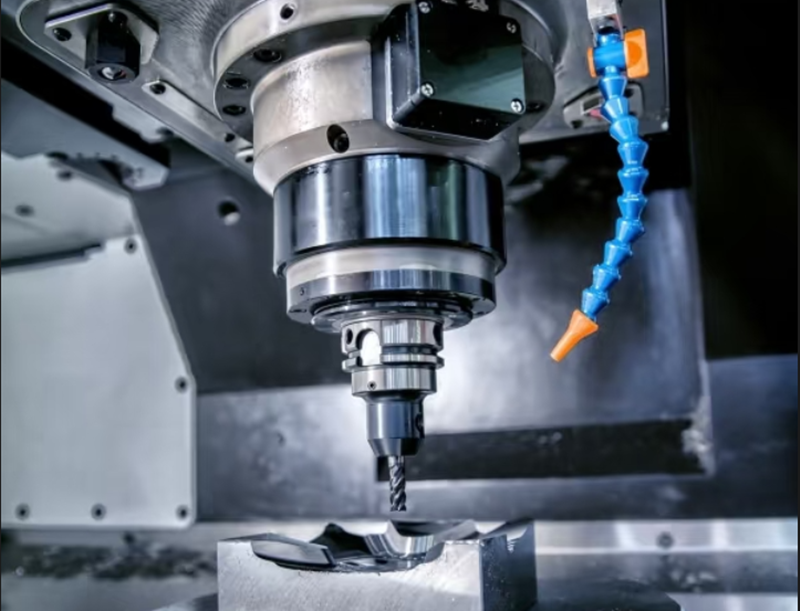

2. Aluminum Machining
Machining, on the other hand, is a specialized process focused on shaping and refining aluminum through material removal. Unlike fabrication, which involves assembly and multi-step processing, machining narrows its focus to achieving precise dimensions and surface finishes.
Key Characteristics of Aluminum Machining:
Scope of Work: Machining involves using tools and machines to remove material from a workpiece to achieve the desired geometry, size, and surface quality.
Purpose: The objective is to achieve extreme precision and detailed features, often for smaller or more intricate parts.
Processes Involved:
Turning: Using a lathe to shape the material by rotating it against a cutting tool.
Milling: Employing a rotating cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece at various angles.
Drilling: Creating precise holes with the help of drill bits.
Grinding: Achieving a fine surface finish and tight tolerances.
Automation and Precision: Modern machining often relies on CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, enabling automated, high-accuracy production. This is particularly advantageous for producing large batches of identical parts.
Applications of Aluminum Machining:
Machining is essential for manufacturing high-precision components like gears, engine parts, and aerospace fittings. It ensures uniformity, fine details, and tight tolerances that are challenging to achieve through other processes.
Key Differences Between Aluminum Fabrication and Aluminum Machining
Integration of Both Processes
In many projects, fabrication and machining complement each other. For instance, a fabricated aluminum frame may require machined components for precision connections or fittings. The synergy between these processes allows manufacturers to leverage the strengths of both, ensuring durability, functionality, and accuracy in the final product.
Understanding these differences enables manufacturers and engineers to select the most appropriate techniques for their specific needs, optimizing cost, time, and quality.