What is the difference between aluminum 7075 vs aluminum 7050?

A Comparison of 7075 and 7050 Aluminum Alloys: Differences, Advantages, and Applications
7075 and 7050 aluminum alloys are two widely used high-strength materials in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and military applications. While they share similar core characteristics, there are significant differences between them in terms of chemical composition, mechanical properties, physical properties, and specific use cases. This article provides an in-depth comparison of the two alloys to help readers understand their key distinctions and advantages.
1. Chemical Composition
Both 7075 and 7050 aluminum alloys are part of the 7xxx series, which are primarily alloyed with zinc, but their specific compositions vary to achieve different performance characteristics.
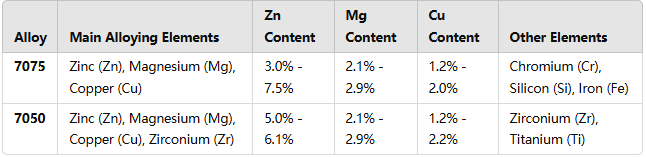
7075 Aluminum Alloy: The key alloying element is zinc, with magnesium and copper playing an important role in strengthening. The zinc content ranges from 3% to 7.5%, which allows the formation of the MgZn2 phase, significantly enhancing the alloy's heat treatment properties.
7050 Aluminum Alloy: Developed to overcome the quenching sensitivity of 7075, 7050 contains increased levels of zinc and copper, as well as a higher Cu/Mg ratio. It also uses zirconium (Zr) instead of chromium (Cr) to improve strength and reduce the likelihood of cracking during heat treatment.
2. Mechanical Properties
7075 and 7050 aluminum alloys differ in terms of mechanical properties, particularly in strength, toughness, and resistance to stress corrosion.
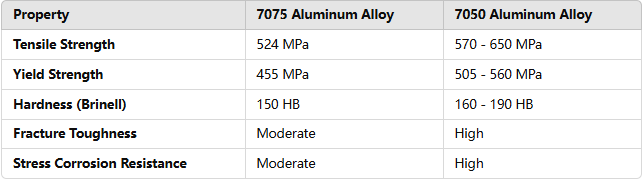
7075 Aluminum Alloy: Known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, 7075 has a tensile strength of up to 524 MPa and a yield strength of 455 MPa. While its hardness is around 150 HB, its resistance to stress corrosion and fracture toughness are moderate.
7050 Aluminum Alloy: The 7050 alloy excels in both tensile strength (up to 650 MPa) and yield strength (up to 560 MPa). It also offers superior fracture toughness and excellent stress corrosion resistance, making it ideal for highly demanding aerospace applications where material integrity is critical.
3. Physical Properties
While the mechanical properties are vital for the strength and durability of the alloy, the physical properties, such as density, thermal conductivity, and electrical properties, also play a significant role in material selection.
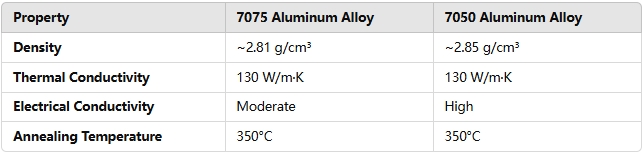
7075 Aluminum Alloy: With a density of about 2.81 g/cm³, 7075 has slightly lower density than 7050. Its thermal conductivity is relatively high, making it suitable for applications requiring heat dissipation.
7050 Aluminum Alloy: The density of 7050 is slightly higher at 2.85 g/cm³, and it has a slightly lower electrical conductivity compared to 7075. However, its stress corrosion resistance is a standout feature that makes it the material of choice in more extreme applications.
4. Application Scenarios
The differences in chemical composition, mechanical properties, and physical characteristics result in distinct applications for 7075 and 7050 aluminum alloys.

7075 Aluminum Alloy: Due to its high strength, 7075 is widely used in aerospace applications, including aircraft parts, landing gear, and military hardware. It also finds use in marine and automotive industries where strength and durability are critical.
7050 Aluminum Alloy: 7050, with its superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and fracture toughness, is especially favored in the aerospace industry for making structural components such as fuselage and wing parts. It is also used in high-performance military and transportation equipment.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages
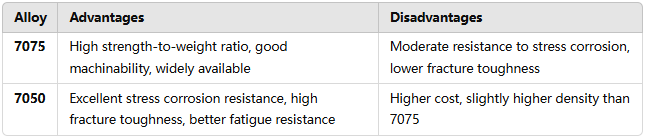
7075 Aluminum Alloy: Its key advantages lie in its high strength and ease of machining, making it a versatile option for a variety of demanding applications. However, it has moderate resistance to stress corrosion and is more susceptible to cracking in highly stressed environments.
7050 Aluminum Alloy: 7050 is known for its excellent performance in critical structural applications, especially where stress corrosion resistance and fracture toughness are paramount. However, its higher cost and slightly greater density might make it less suitable for cost-sensitive applications.
6. Conclusion
Both 7075 and 7050 aluminum alloys offer exceptional strength and performance, but they serve different needs. 7075 is an excellent choice for applications requiring high strength and good machinability, such as in aerospace, military, and automotive industries. On the other hand, 7050 excels in environments that demand superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and greater fracture toughness, making it particularly suited for structural components in aerospace and military applications.
By understanding the key differences between these two alloys, engineers and manufacturers can select the right material based on the specific requirements of their projects. Whether it’s the higher strength and lower cost of 7075 or the superior corrosion resistance and toughness of 7050, both alloys are crucial in high-performance applications where material integrity is of utmost importance.